Global Positioning System (GPS) is no stranger to us. Whether it’s navigating when going out, tracking workouts, or monitoring package deliveries, we can’t live without it. As a core tool for “finding directions, timing, and locating positions” in modern life, GPS has been upgrading rapidly. Since 2024, with improved chip technology, better collaboration between multiple navigation systems, and the growing demand for “intelligence” across various industries, GPS has made significant breakthroughs in both technology and applications—not only making daily positioning more convenient but also expanding into many new scenarios.
GPS Chips: Smaller, More Power-Efficient, and Portable Devices More Useful
Chips are like the “brain” of GPS devices. Their performance directly affects positioning accuracy, device size, and battery life. In the first half of 2024, many chip manufacturers launched a new generation of GPS-specific chips. The biggest improvements are “smaller size” and “lower power consumption,” making small, portable GPS devices more popular than ever.
For example, a new GPS chip from a well-known semiconductor company uses advanced 7nm manufacturing technology. Compared to the previous generation, it’s 35% smaller in size and 40% more energy-efficient, with positioning accuracy within 1 meter in open areas. This chip eliminates unnecessary structures from traditional chips and optimizes the satellite signal reception module. Even in cities blocked by high-rise buildings or with weak signals, it can quickly capture satellite signals—no more waiting ages to get a fix.
Today, this new chip is used in many products:
- New smart bracelets equipped with it can accurately track workout routes while offering a battery life of over 15 days, completely solving the old problem of “either accurate positioning but poor battery life, or long battery life but inaccurate positioning.”
- In the industrial sector, small, power-efficient GPS chips are installed in IoT devices, helping factories precisely locate machinery, remotely monitor equipment status, and reduce maintenance costs.
Autonomous Driving Gets “Precise Navigation”: Centimeter-Level Positioning for Greater Safety
Reliable autonomous driving relies heavily on accurate positioning, and GPS is one of the core positioning tools. In 2024, GPS has made major progress in autonomous driving—through deep integration with RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) technology and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), it now achieves “centimeter-level” positioning, solving the key issues of “inaccurate positioning and slow response” in previous autonomous driving systems.
Previously, traditional GPS could only achieve meter-level accuracy in autonomous driving, which was far from sufficient for high-speed travel or complex road conditions. For example, slight positioning errors during turns, lane-keeping, or obstacle avoidance could lead to safety accidents. The new “GPS + RTK” integrated positioning solution launched in 2024 receives correction signals from base stations to calibrate GPS satellite signals, achieving positioning accuracy of ±1 cm horizontally and ±2 cm vertically, with a response time of less than 10 milliseconds.
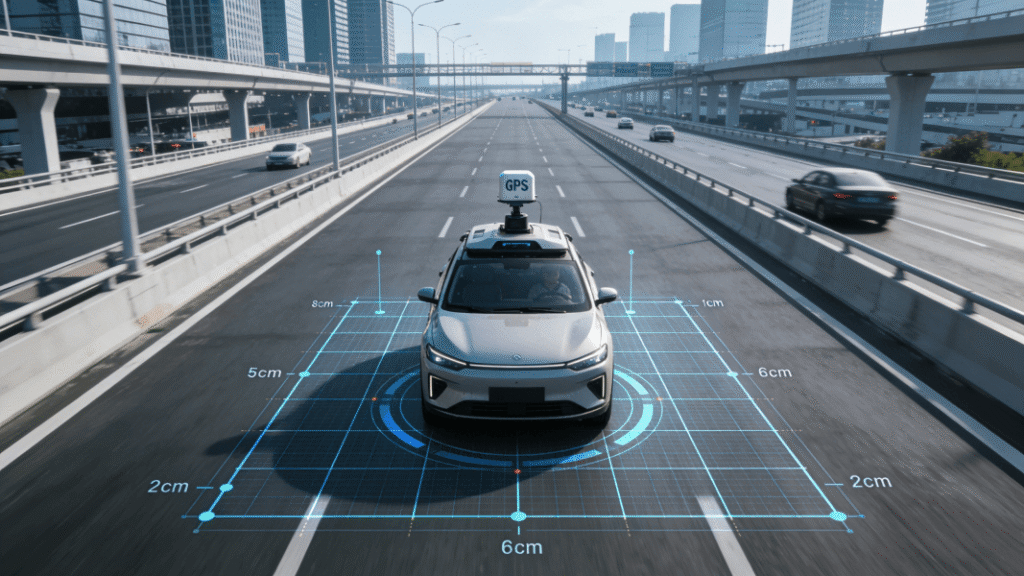
Many domestic automakers have now adopted this solution in high-end autonomous driving models, covering both highway and urban road scenarios. For instance, a new autonomous driving model from a new energy vehicle brand, equipped with this system, can accurately identify lane lines and road signs. Even in severe weather like heavy rain or heavy fog, positioning remains stable, greatly enhancing the safety of autonomous driving. Additionally, this solution is used in smart logistics trucks and driverless shuttles, helping the logistics and transportation industries improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
Beidou + GPS: Working Together for More Reliable, Wider Coverage
Using only the GPS system has limitations—for example, in remote mountainous areas, the open sea, or high altitudes, weak satellite signals can lead to inaccurate or interrupted positioning. In 2024, the collaboration between China’s Beidou Navigation System and GPS has become increasingly mature. Working together, the two systems “complement each other’s shortcomings and double accuracy,” resulting in more reliable positioning and wider coverage—a major trend in GPS applications.
The advantages of Beidou-GPS integration are clear:
- Beidou’s geostationary satellites compensate for GPS’s insufficient signal coverage in low-latitude regions.
- GPS’s medium Earth orbit satellites improve Beidou’s positioning accuracy in high-latitude areas.
Through specialized algorithms, devices can receive signals from both systems simultaneously and automatically select the strongest signal for positioning. Even if one system’s signal is interrupted, the other can take over, increasing positioning reliability by over 80%.
Today, this integrated positioning is used in many fields:
- Ocean-going ships equipped with it can achieve precise positioning at sea, avoiding course deviations and reef collisions.
- Agricultural machinery uses it for precise sowing, fertilization, and harvesting, making agricultural production more efficient.
- During emergency rescues, positioning terminals carried by rescuers can quickly locate trapped people in complex terrains like mountains and forests, shortening rescue time and improving success rates.
New GPS Features in Consumer Electronics: Safer Outdoor Adventures
Consumer electronics like mobile phones and smartwatches are among the most common uses for GPS. As people grow more fond of outdoor adventures and fitness, there’s a growing demand for higher positioning accuracy and more diverse features in these devices. In 2024, major manufacturers have focused on innovating GPS functions—especially in smartwatches, which now offer more accurate positioning and practical features, perfect for outdoor enthusiasts.



Previously, ordinary smartwatches had GPS accuracy of only 5-10 meters, which was inadequate for activities like hiking, trekking, and camping. The 2025 new outdoor smartwatches, however, optimize GPS signal reception modules and add auxiliary tools like barometers and compasses, achieving positioning accuracy within 3 meters. They also include new features such as track playback (to review routes), altitude positioning, and offline map navigation—comprehensively supporting outdoor scenarios.
For example, a new outdoor smartwatch from a well-known brand, equipped with an upgraded GPS module, can accurately record hiking routes and altitude changes. Even in remote mountainous areas without network coverage, it can navigate using offline maps. It also supports dual-system positioning (Beidou + GPS), ensuring positioning won’t be lost even if one system’s signal is weak. Additionally, some watches include a GPS emergency call feature—if you encounter danger outdoors, you can send precise positioning information to help rescuers find you quickly.

Beyond smartwatches, mobile phones and action cameras also feature new GPS functions:
- New mobile phones can locate you in less than 1 second, even indoors (e.g., malls, subway stations), helping you find stores or exits quickly.
- Action cameras with GPS can record shooting routes and speeds, adding more details to your workout or adventure records.
From smaller, more power-efficient chips to centimeter-level positioning for autonomous driving, from Beidou-GPS integration to new features in consumer electronics—every progress in the GPS industry in 2024 has made positioning more accurate, reliable, and convenient. In the future, as technologies like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and 5G integrate deeply with GPS, GPS will expand into more new fields, bringing greater convenience to our work and daily lives.